|

|
|
win 1251 |
| |
|
Dictionaries
Our experience shows, that the more carefully dictionaries
in the machine translation system are customized, the higher
is the system's translation quality, and the easier for users
is editing or reading a resulting text. For this purpose, within
our centre we created our own specialized dictionaries for topics
as follows:
Real number of dictionaries is much bigger than that of topics
mentioned since, for example, for telecommunications there are
several dictionaries - switching, transmission systems, intelligent
networks, ATM, mobile communication etc. In addition, a creation
of new dictionaries and a customization of existing ones is
possible according to terminology requirements or customer's
demands.
Contents of specialized dictionaries
Usually, a general lexicon which is necessary for translations
is already available in the general dictionary (it is supplied
together with a machine translation system). The following information
is entered into specialized dictionaries:
-
basic
terminology (for example, for such subjects as hardware and
software, telecommunications, mechanics, power supply, etc.)
-
terminology,
specific to documentation under translation (names for modules,
units, devices, programs; extension of abbreviations; specific
slang etc.)
-
frequently occured expressions/phrases/sentences
(so called microsegments), for example:
- it is assumed that
- if otherwise not specified
- note that
- the following window is appeared
Sources of terms for specialized dictionaries
-
international recommendations
and standards (ITU-T, ETSI)
-
existing dictionaries
(hardcopy and electronic)
-
articles in the periodicals,
containing a terminology (with explanations)
-
explanatory dictionaries
with terms and abbreviations of manufacturers
-
documentation itself
Difference between general and specialized
dictionaries
If you will take in your hands any general-purpose
dictionary (for example, English-to-Russian, Russian-to-German,
Spanish-to-Italian and so forth), you will realize that the
main share of terms is made with single words (common nouns,
adjectives, adverbs and verbs). A number of word collocations
is always less.
The different case is with specialized dictionaries
(for example, polytechnical, legal, for computer technologies
and so forth). As a rule, main terms are word collocations,
containing two and more words.
In a figure below, the contents of our dictionaries
for machine translation systems (number of dictionary entries
with one, two, three and more words) is shown in a percentage.
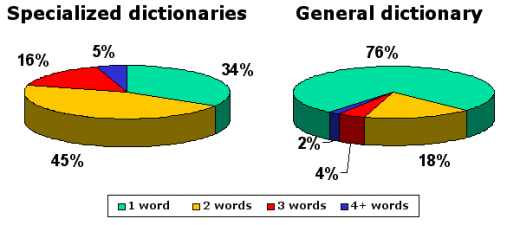
If in the general dictionary (general-purpose),
minimum two thirds of terms are single words, so in specialized
and user dictionaries main share (over 50%) is for word collocations
of several words.
Dictionary customization
For a high-quality dictionary customization
it is necessary to:
-
know a subject of translation
-
know basic grammar rules
(of both languages)
-
continously add and update
the dictionary (an ultimate goal is that the system output
must be "predictable")
By its contents, dictionaries for machine translation
systems are similar to conventional ones (for example, in hardcopy).
However, there are specific features:
-
It is necessary to enter
word collocations in a plural number.
-
It is necessary to "struggle"
with homonyms. For example, the term list (as a verb and noun).
If the word collocation "device list" is not entered,
a phrase "device lists" can be translated not correctly
by sense, but correctly by grammar. Then, it is necessary
to enter into the dictionary a marked word collocation (in
plural).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|